Exploring the efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells involves considering various factors like cost, environmental impact, and energy efficiency. We will also take a look at the benefits of Lithium-ion batteries as a superior alternative to hydrogen fuel cells according to a source at Tiny House 43.
Energy efficiency
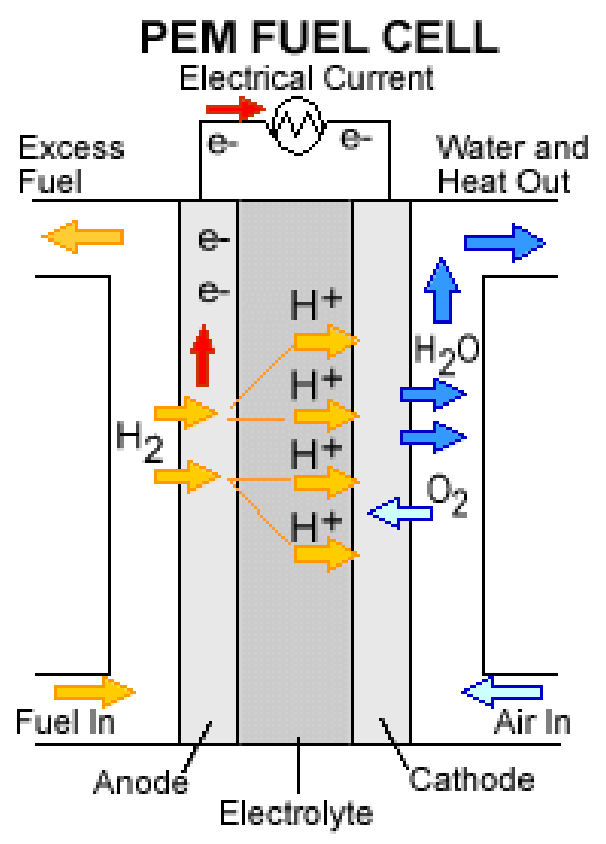
Energy efficiency is one of the most important parameters when it comes to the design of fuel cells. There are many ways to assess the fuel cell’s energy efficiency. One way to determine its power size is to do so. Normally, a fuel cell uses pipeline natural gas as its hydrogen source. Some fuel cells can also use biogas, which comes from wastewater treatment.
Another way to evaluate the energy efficiency of a fuel cell is to compare it to the efficiency of a conventional combustion-based car. A conventional combustion-based car typically operates at a maximum efficiency between twenty and thirty percent. A hydrogen fuel cell, however, will operate at 40-60 percent efficiency. This is significantly higher than standard fuel cars. The car’s size and road conditions will also affect the efficiency.
You can also compare the energy efficiency of hydrogen fuel cell by looking at how much energy they use to run a car. A typical fuel cell vehicle consumes 0.8 kg of hydrogen per 100 km – this is the equivalent of almost five litres of petrol. A hydrogen fuel cell vehicle can usually drive for 500 km before it needs refilling. This is a lot more than the range of an electric car.
Cost
Several companies in the hydrogen industry are rapidly scaling up production. Some of them are manufacturing fuel cells exclusively for the auto industry, while others are making them for other purposes, such as home use. However, hydrogen fuel cells can have some serious drawbacks that can make them prohibitively costly. One of the biggest drawbacks is safety. Hydrogen is highly flammable, and can easily spread openly.
The majority of hydrogen in the world comes from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. Electrolysers heat water with electricity to make hydrogen. But this process is expensive, and it also leads to efficiency losses. This means that hydrogen fuel cells will not be cost-effective for the average consumer.
The cost of hydrogen produced through electrolysis has decreased by 60% in the past seven years. In 2010, the cost was between USD $10-$15 per kilogram. It currently costs $4-$6 per kilogram and is expected to drop further. According to industry reports, there will be continued cost reduction. McKinsey’s study shows that hydrogen produced using this method will be cheaper by 60% by 2030.
Environmental impact
Although hydrogen fuel cells are extremely efficient, their environmental impact can be problematic. Hydrogen emissions are six times higher than those from the burning of methane, and they have serious health effects, including an increased risk of respiratory infections and asthma. They can also be precursors to ozone or particulate matter, which can cause respiratory problems. However, there are ways to limit the pollution generated by hydrogen fuel cells.
One problem with hydrogen fuel cells is that it’s not always clean to produce. The process of extracting hydrogen from water is costly, and it consumes fossil fuels. Hydrogen production can also result in the release of carbon dioxide. This can have a negative effect on the ozone layer. Hydrogen leakage can also worsen global warming.
Other issues with hydrogen fuel cells are that it’s expensive to produce and difficult to transport. It must be stored under high pressure. As a result, researchers at the California Institute of Technology estimate that up to 20% of hydrogen will leak into the atmosphere. This oxidized hydrogen can affect the ozone layer, stratosphere, and polar vortex.
Lithium-ion battery advantage
Today, lithium-ion battery technology is becoming more popular in electric vehicles and consumer electronics. The hydrogen we use in fuel cells is also a potential energy storage medium. Hydrogen can be used in transportation, the supply of energy to buildings, and long-term grid storage. As a result, hydrogen will likely play a key role in the decarbonization of our electricity supply.
The long range of hydrogen-powered vehicles is another advantage. Because hydrogen provides hundreds of times the energy density of gasoline, hydrogen-powered cars can drive a longer distance before needing to refuel. Fast charging with hydrogen is possible, as it can provide up to 80% power in just 30 minutes. A regular AC charger can take up to five hours to fully charge an electric vehicle. A lithium-ion battery is limited in its ability to handle fast-charge cycles before it runs out of capacity.
The performance of batteries is greatly affected by effective heat dissipation. The heat generated by batteries affects battery life, safety, and reliability. To manage heat in batteries, external cooling systems are used. This leads to complex system designs and lower energy density.
Expensive materials required
Hydrogen fuel cells are a growing energy technology that have the potential to significantly reduce the nation’s dependence on fossil fuels. They produce clean, renewable energy that has no adverse environmental impact and do not require large amounts of land. They can also be scaled down economically to make energy from very small amounts. They are ideal for portable power and transportation. As a result, the European Commission and other organizations are working to develop hydrogen fuel cells in Europe.
Hydrogen fuel cells have an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. The electrodes in hydrogen fuel cells are made of platinum, which is very expensive but has excellent catalytic properties. There are cheaper alternatives available, such as alkaline-polymer electrolyte fuel cells. These use less expensive materials, but don’t have the same performance or durability as platinum.
Scientists have been searching for a catalyst that would reduce the cost of hydrogen fuel cells. The catalyst’s cost is the main obstacle to the development of these energy systems. Platinum is extremely expensive and can be difficult to come by. However, if a more affordable catalyst could be developed, hydrogen fuel cells could become a mainstream source of energy.
Blue hydrogen versus fossil fuels
When evaluating blue hydrogen as a fuel for hydrogen fuel cells, it is important to keep in mind that it contains more carbon than other fossil fuels. It is 28 to 36 times more powerful than CO2 in global warming and is approximately 28 to 35 times more potent. One molecule of methane in the atmosphere is equivalent to about 30 molecules of CO2. This is a critical issue that hydrogen fuel cell developers must address.
Blue hydrogen is promoted by the gas industry as a climate-friendly option to fossil fuels. However, both fuels actually produce carbon dioxide when they are burned. Blue hydrogen captures the most CO2, while green hydrogen can capture up to 85 per cent of the carbon dioxide that is released to the atmosphere. Even a small amount of carbon can have significant impacts on climate change. Still, advocates for blue hydrogen argue that it is cheaper and will have a significant role in hydrogen production.
In the United Kingdom, the debate over blue hydrogen has been heated by the contrasting views of activists and politicians. In Scotland, a campaigner with Friends of the Earth Scotland has said that the technology is unsuitable for heating homes with hydrogen, as it will allow fossil fuel companies to remain in business. The UK government, on the other hand, has accepted hydrogen technology as an alternative for fossil fuels. However, some argue that it should not be used to heat homes.
Green hydrogen uses fossil fuels but captures CO2 emissions
Green hydrogen fuel cells are a promising alternative energy source. This is the first step towards addressing climate change. Hydrogen can be used to replace oil and gas in mobile energy, and it is also a cleaner fuel than traditional fossil fuels. But it must be priced competitively with gas to be commercially viable. The price gap between green and natural gas must be closed by policymakers. Contracts for Difference (CfDs), which are available for green hydrogen, can be implemented.
Currently, most hydrogen is produced through steam methane reforming, a process that uses a catalyst to react methane with high-temperature steam. The reaction results in hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The carbon monoxide is filtered out, leaving pure hydrogen. You can also use other fossil fuels in this process. However, the carbon emissions produced by this process are high, and the process is not carbon-neutral.
Green hydrogen is not the best option to create a carbon-free economy but it is a great solution for moving and storing renewable energy. For example, it can be used in marine shipping and aviation to store intermittent renewable energy and transport it around the world. It can also be used in industrial processes as a feedstock.