Beginners Guides
How Many Kw Does A Tiny House Use

Step into the tiny house universe, where small homes harbor giant ambitions. Our adventure dives into the intriguing world of how little these cozy homes use energy.
Like a hummingbird sipping nectar from a flower, tiny houses gracefully sip electricity to power their essential needs.
In this article, I will guide you through the intricacies of understanding and optimizing energy usage in tiny houses. We will explore the factors that influence this consumption, calculate average energy needs, and debunk common myths surrounding it. Through real-life case studies, we will witness the awe-inspiring feats of energy-efficient dwellings.
Living sustainably is not just an aspiration; it is a responsibility towards our planet. By embracing low-energy housing options like tiny houses, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
So join me as we uncover the secrets behind how many kilowatts (KW) a tiny house uses. Together, we will unlock the power of knowledge and empower ourselves to make informed choices for sustainable living.
Key Takeaways
- Factors influencing energy consumption in tiny houses include house size, insulation, and the type of appliances used.
- Strategies for saving energy in tiny houses include proper insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, and the use of energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy sources.
- Energy efficiency factors in tiny houses include design, construction materials, and the use of renewable energy sources.
- Transitioning to sustainable living through tiny houses can help reduce carbon footprint and contribute to sustainable living.
Understanding Tiny House Energy Consumption
You might be wondering how much power a tiny house actually uses. Well, let’s dive into the world of tiny house energy consumption.
There are several factors that influence energy usage in these small dwellings. First and foremost is the size of the house itself. Tiny houses typically range from 100 to 400 square feet, so they require significantly less energy compared to traditional homes.
Another important factor is insulation. Proper insulation helps to regulate temperature inside the tiny house, reducing the need for heating or cooling appliances and consequently saving energy. Additionally, efficient windows and doors play a crucial role in minimizing heat transfer.
The type of appliances used also affects energy consumption. Energy-efficient appliances like LED lights, low-flow water fixtures, and ENERGY STAR-rated electronics can significantly reduce overall power usage.
Furthermore, renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines are increasingly popular among tiny homeowners as they provide sustainable electricity while reducing dependence on the grid.
There are several strategies that can help save energy in a tiny house: proper insulation, use of energy-efficient appliances, and harnessing renewable energy sources.
In the next section, we will explore in detail the factors that influence energy usage in tiny houses without repeating what has already been discussed thus far.
Factors that Influence Energy Usage in Tiny Houses
One interesting statistic is that the size of a tiny house directly affects its energy consumption. There are several factors that influence the energy usage in tiny houses, which can be categorized into two main categories: factors affecting energy efficiency and cost-saving strategies.
Firstly, the design and construction materials used in a tiny house play a significant role in its energy efficiency. Proper insulation, high-quality windows, and efficient heating and cooling systems can greatly reduce energy consumption. Additionally, incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines can further maximize energy efficiency.
Secondly, lifestyle choices and daily habits also impact the amount of energy consumed in a tiny house. Being mindful of electricity usage by turning off lights when not needed and using energy-efficient appliances can contribute to significant savings. Furthermore, adopting sustainable practices like composting or using rainwater for gardening can help reduce overall water and energy usage.
By considering these factors affecting energy efficiency and implementing cost-saving strategies, owners of tiny houses can minimize their environmental footprint while enjoying comfortable living spaces that require minimal amounts of energy.
In the next section about calculating the average energy consumption of a tiny house, we will delve into specific methods to determine the precise amount of kilowatts used by these compact dwellings without compromising on modern amenities.
Calculating the Average Energy Consumption of a Tiny House
To calculate how much energy your tiny home consumes on average, start by examining its daily habits and lifestyle choices. The key to accurately estimating energy consumption is to consider all the factors that contribute to it.
Begin by assessing the types of appliances and electronics in your tiny house. Energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce power usage, so make sure to invest in those with high Energy Star ratings.
Next, evaluate the insulation and weatherization of your home. Properly insulated walls, windows, and doors can prevent heat loss or gain, reducing the need for heating or cooling systems. Additionally, consider implementing smart technology such as programmable thermostats or motion sensors that automatically turn off lights when not in use. These small adjustments can greatly impact energy costs over time.
By calculating energy costs based on appliance usage and incorporating energy-efficient practices into your daily routine, you can optimize energy efficiency in your tiny house without compromising comfort or convenience.
Now let’s move on to some tips for optimizing energy efficiency in tiny houses…
Tips for Optimizing Energy Efficiency in Tiny Houses
Implementing energy-efficient practices and utilizing smart technology can greatly enhance the efficiency of energy usage in your compact living space. To maximize insulation, start by ensuring that your tiny house is properly sealed to prevent air leakage. Use high-quality insulation materials like spray foam or rigid foam boards to create a tight building envelope.
Additionally, consider installing double-pane windows with low-emissivity coatings to reduce heat transfer.
In terms of appliances, make sure to choose energy-efficient options. Look for appliances with the ENERGY STAR label, as they’re designed to consume less electricity without sacrificing performance. Opt for LED lighting throughout your tiny house, as they use significantly less energy compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
Another way to optimize energy efficiency is by using smart home technology. Smart thermostats allow you to control and schedule the heating or cooling of your tiny house remotely, ensuring that you only use energy when necessary. Smart power strips can also help eliminate standby power consumption by automatically cutting off power to devices not in use.
By maximizing insulation and using efficient appliances, you can significantly reduce your tiny house’s energy consumption. Transitioning into the subsequent section about common myths about tiny house energy usage, it’s important to debunk misconceptions and provide accurate information on how these small dwellings utilize electricity efficiently without compromising comfort or convenience.
Common Myths about Tiny House Energy Usage
Contrary to popular belief, living in a tiny house doesn’t mean sacrificing comfort or convenience when it comes to energy usage. There are several common myths surrounding the energy consumption of tiny houses that need debunking. One myth is that tiny houses use significantly less electricity than traditional homes. While it’s true that tiny houses have a smaller footprint, they still require power for essential appliances and amenities.
To illustrate this point, let’s take a look at a comparison between the average energy consumption of a tiny house and a traditional home. In the table below, you can see the estimated kilowatt-hours (kWh) used per day for various appliances:
| Appliance | Tiny House (kWh/day) | Traditional Home (kWh/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| Air Conditioner | 2 | 4 |
| Lighting | 0.5 | 1 |
| Water Heater | 3 | 6 |
As you can see, while there are some differences in energy usage, the gap isn’t as significant as one might think. Tiny houses still require electricity for essential appliances such as refrigerators and lighting.
In the next section, we will delve further into comparing the overall energy consumption of tiny houses and traditional homes. It is important to consider all factors before making any assumptions about their respective efficiency levels without conducting an in-depth analysis.
Comparing Energy Consumption of Tiny Houses and Traditional Homes
When comparing energy consumption, it’s interesting to note the differences between tiny houses and traditional homes.
Several factors affect the energy usage of a tiny house, making it more efficient than its larger counterpart. Firstly, the smaller square footage of a tiny house means there is less space to heat or cool, resulting in reduced energy needs. Additionally, many tiny houses are designed with energy-saving techniques in mind. These include using high-quality insulation materials to minimize heat transfer and employing double-pane windows to prevent drafts.
Furthermore, tiny houses often utilize renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines. This not only reduces their reliance on traditional power grids but also helps lower their overall energy consumption. In fact, some well-designed and properly equipped tiny houses can achieve net-zero energy status.
By incorporating these various techniques and technologies into their design and construction, tiny houses can significantly reduce their environmental impact while still providing comfortable living spaces.
Case studies: real-life examples of energy-efficient tiny houses will further illustrate how these strategies have been successfully implemented.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about case studies: real-life examples of energy-efficient tiny houses…
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Energy-Efficient Tiny Houses
Transitioning to case studies, we can see real-life examples of how energy-efficient tiny houses have successfully incorporated various techniques and technologies to minimize their environmental impact while still providing comfortable living spaces. These case studies serve as tangible proof that energy-efficient design is not only achievable but also practical for those seeking a sustainable lifestyle.
Here are three remarkable examples:
-
The Eco-Capsule: This innovative tiny house utilizes solar panels and a built-in wind turbine to generate electricity, making it completely self-sufficient. With its rainwater collection system and composting toilet, the Eco-Capsule minimizes water consumption and waste production.
-
The ZeroHouse 2.0: Designed with energy efficiency in mind, this tiny house integrates advanced insulation, high-performance windows, and an air-tight building envelope to reduce heating and cooling demands significantly. Additionally, it features a rooftop solar array that provides renewable energy for all household needs.
-
The Leaf House: Built with reclaimed materials and equipped with Energy Star-rated appliances, this tiny house exemplifies sustainability. Its passive solar design maximizes natural light and heat gain while minimizing energy consumption.
These real-life examples showcase the potential of energy-efficient tiny houses to minimize resource usage without compromising comfort or convenience. By adopting such designs on a larger scale, we can collectively contribute to reducing our carbon footprint and preserving the environment for future generations.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about the ‘environmental benefits of living in a low-energy tiny house,’ we unveil further advantages beyond just reduced energy consumption.
Environmental Benefits of Living in a Low-Energy Tiny House
Living in a low-energy tiny house offers a range of environmental benefits, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to preserving natural resources and promoting sustainable living. These homes are designed to minimize energy consumption through various energy-saving techniques and the use of green building materials.
One key aspect of low-energy tiny houses is their efficient insulation. By using materials such as cellulose or spray foam insulation, these homes can significantly reduce heat transfer and maintain stable indoor temperatures without relying on excessive heating or cooling systems. Additionally, high-quality windows with double or triple glazing help to prevent heat loss during winter months and keep the interior cool during summer.
Another important feature is the integration of renewable energy sources into the design. Solar panels are commonly installed on the roof of tiny houses to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuels. These solar-powered systems can generate enough electricity to power essential appliances and lighting within the house.
Furthermore, low-energy tiny houses often incorporate rainwater harvesting systems for water conservation purposes. The collected rainwater can be used for tasks like irrigation or toilet flushing, reducing the demand for freshwater resources.
Living in a low-energy tiny house not only reduces carbon emissions but also promotes sustainable practices by utilizing energy-saving techniques and green building materials. Transitioning into tools and resources for monitoring and reducing energy usage allows homeowners to further optimize their environmental impact without compromising comfort or convenience.
Tools and Resources for Monitoring and Reducing Energy Usage
To truly harness the power of sustainability, you need to equip yourself with the tools and resources that act as your energy-saving superpower. When it comes to living in a tiny house, every kilowatt matters. Luckily, there are various energy-saving techniques and smart home technologies available that can help you monitor and reduce your energy usage.
Here are five essential tools and resources to consider:
-
Energy monitoring systems: These devices allow you to track your energy consumption in real-time, helping you identify areas where you can make adjustments for optimal efficiency.
-
Smart thermostats: With programmable features and remote control capabilities, these thermostats enable you to regulate heating and cooling based on occupancy patterns or time of day.
-
LED lighting: By replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED lights, you can significantly reduce electricity usage without compromising on brightness or quality.
-
Solar panels: Installing solar panels on your tiny house’s roof allows you to generate clean, renewable energy while reducing reliance on the grid.
-
Energy-efficient appliances: From refrigerators to washing machines, choosing appliances with high Energy Star ratings ensures they consume less electricity.
By incorporating these energy-saving tools and techniques into your tiny house lifestyle, you can achieve significant reductions in your overall energy consumption. Embracing sustainable living in tiny houses means embracing a greener future where our homes work harmoniously with the environment.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Living in Tiny Houses
Equip yourself with the essential tools and resources for embracing sustainable living in your tiny house, and watch as your energy consumption decreases and your home becomes a greener, more efficient haven. Embracing a sustainable lifestyle in a tiny house brings numerous benefits.
Not only does it reduce our carbon footprint and help protect the environment, but it also saves us money in the long run. By implementing energy-efficient appliances and using renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines, we can significantly reduce our dependence on traditional power grids. Monitoring our energy usage through smart meters allows us to identify areas where we can make further improvements. These tools provide real-time data on electricity consumption, helping us understand how our actions impact energy usage.
Reducing waste is another crucial aspect of sustainable living in tiny houses. Utilizing composting toilets, rainwater harvesting systems, and recycling practices ensures that minimal waste is generated. Additionally, incorporating insulation materials made from recycled or renewable resources helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures without excessive use of heating or cooling systems.
Embracing a sustainable lifestyle not only benefits us individually but also contributes to the greater good by conserving natural resources for future generations. It fosters self-sufficiency while promoting environmental stewardship within the tiny house community.
So let’s equip ourselves with these essential tools and resources, embrace sustainable living in our tiny houses, and enjoy the many benefits it brings both to ourselves and to the planet we call home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are tiny houses more energy-efficient than traditional homes?
While tiny houses may seem more energy-efficient due to their smaller size, this is not always the case. However, many tiny houses are built with energy-efficient design principles in mind, such as better insulation and efficient appliances.
These features can lead to significant cost savings in terms of energy consumption. Therefore, when designed properly, tiny houses have the potential to be more energy-efficient than traditional homes and provide long-term financial benefits.
What are some common misconceptions about energy usage in tiny houses?
Common misconceptions about energy usage in tiny houses include the belief that they consume significantly less energy compared to traditional homes. While their compact size and efficient design can reduce energy consumption, factors such as climate, insulation, appliances, and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role.
It’s important to consider these factors when estimating the energy needs of a tiny house. Understanding these misconceptions helps individuals make informed decisions about optimizing energy efficiency in their tiny homes.
How can I measure and monitor the energy usage in my tiny house?
To measure and monitor energy usage in my tiny house, I rely on various tools and techniques. Firstly, I use smart meters to track electricity consumption in real-time. These meters provide accurate data on kilowatt-hour usage, allowing me to identify patterns and make informed decisions about energy conservation.
Additionally, I employ energy monitoring systems that offer detailed insights into power usage across different appliances. By diligently measuring and tracking my energy consumption, I can optimize efficiency and reduce unnecessary wastage.
What are some practical tips for reducing energy consumption in a tiny house?
To reduce energy consumption in a tiny house, I recommend implementing some practical tips. First, focus on insulation to minimize heat loss or gain.
Next, utilize energy-efficient appliances and LED lighting to lower electricity usage.
Additionally, consider using natural light during the day and installing solar panels for renewable energy generation.
Finally, adopt smart home technology to monitor and control energy usage more effectively.
These tips can significantly reduce energy consumption in your tiny house.
Are there any financial incentives or tax credits available for energy-efficient tiny houses?
Yes, there are several financial incentives and tax credits available for energy-efficient tiny houses. These incentives aim to promote sustainable living and reduce carbon emissions.
Some examples include federal tax credits for renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines, as well as state-level incentives like grants or rebates for energy-efficient appliances and insulation.
Taking advantage of these incentives can help offset the initial costs of building or retrofitting a tiny house to be more energy efficient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, after diving into the world of tiny house energy consumption, it’s clear that these small dwellings can have a big impact on our carbon footprint.
By optimizing energy efficiency and embracing sustainable living practices, we can minimize our environmental impact while still enjoying the comforts of home.
From monitoring tools to case studies of real-life examples, there are plenty of resources available to help us reduce our energy usage in these tiny spaces.
So let’s take a leap into the world of low-energy living and make a difference for our planet!
Hi, I’m Emma. I’m the Editor in Chief of Tiny House 43, a blog all about tiny houses. While tree houses are often associated with childhood, they can be the perfect adult retreat. They offer a cozy space to relax and unwind, surrounded by nature. And since they’re typically built on stilts or raised platforms, they offer stunning views that traditional homes simply can’t match. If you’re looking for a unique and romantic getaway, a tree house tiny house might just be the perfect option.
Beginners Guides
How Big Is The Tiny House On Ashland

Did you know that the average size of an American household is around 2,600 square feet? Residing in such a limited space may seem difficult to imagine, but that was exactly my situation during my time at the tiny house in Ashland.
This unique home is a perfect example of maximizing space and living a minimalist lifestyle. With its sleek design and compact footprint, the tiny house on Ashland offers a glimpse into a different way of living.
In this article, we will explore just how big (or should I say small) this tiny house really is. We’ll take a look at the exterior dimensions, interior layout, and innovative storage solutions that make this tiny house a functional and comfortable living space.
So, join me as we discover the world of tiny living in the tiny house on Ashland.
Key Takeaways
- The exterior dimensions of the tiny house on Ashland are 20 ft length, 8.5 ft width, and 13.5 ft height.
- The interior layout maximizes space and creates a cozy atmosphere with a lofted sleeping area, compact kitchen, and multi-purpose living area.
- The tiny house features clever storage solutions, custom-built shelves, and multifunctional furniture to maximize space and minimize clutter.
- Living in a tiny house on Ashland promotes a minimalist lifestyle, cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and a smaller carbon footprint.
Exterior Dimensions
So, how big is the tiny house on Ashland? Well, let’s start by talking about its exterior dimensions.
The tiny house on wheels is designed with a minimalist approach, focusing on simplicity and functionality. Measuring at 20 feet in length, 8.5 feet in width, and 13.5 feet in height, this compact dwelling offers a surprisingly spacious living experience.
The exterior is constructed with durable and lightweight materials, ensuring both durability and mobility. With its sleek and modern design, the tiny house on Ashland stands out among traditional homes, making it a perfect choice for those seeking a unique and eco-friendly lifestyle.
The minimalist design not only maximizes the available space but also allows for easy customization to fit individual preferences and needs.
As we transition into the subsequent section about the interior layout, you’ll discover how every square inch of this tiny house has been thoughtfully utilized to provide comfort and functionality.
Interior Layout
The interior layout of the small dwelling on Ashland is designed to maximize space and create a cozy atmosphere. Every inch of the tiny house design has been carefully thought out to ensure efficient use of space. Here are three key features that contribute to the overall functionality and comfort of the interior:
-
Lofted sleeping area: The tiny house features a lofted sleeping area that allows for a separate space dedicated solely to rest. This not only saves valuable floor space but also creates a sense of privacy and coziness.
-
Compact kitchen: The kitchen in the tiny house is designed to be compact yet fully functional. It includes a small refrigerator, a two-burner stove, and a sink. The use of space-saving storage solutions like built-in shelves and cabinets ensures that all essential kitchen items can be easily stored and accessed.
-
Multi-purpose living area: The living area in the tiny house serves multiple purposes. It can be used as a seating area during the day and easily converted into a dining space or a work area when needed. The flexible nature of the living area allows for maximum use of the available space.
The interior layout of the small dwelling on Ashland is just the beginning of the clever space optimization in this tiny house. The next section will explore the innovative use of multifunctional furniture to further enhance the functionality and versatility of the space.
Multifunctional Furniture
Get ready to be amazed by the incredible ways multifunctional furniture can transform a cramped living space into a practical and stylish oasis. In the tiny house on Ashland, every square inch is utilized to its fullest potential, thanks to space-saving solutions and minimalist design. The furniture in this tiny house isn’t just functional but also versatile, serving multiple purposes to maximize the limited space available.
One example of multifunctional furniture in the tiny house is the sofa that can be converted into a bed. During the day, it provides comfortable seating for relaxation or entertaining guests. At night, it effortlessly transforms into a cozy sleeping area, saving valuable space that would otherwise be taken up by a separate bed.
Another ingenious piece of furniture is the dining table that can be folded and tucked away when not in use. This allows for more open space in the living area, creating a sense of openness and airiness.
Multifunctional furniture not only saves space but also adds a touch of style to the tiny house. The designers have carefully chosen pieces that aren’t just functional but also aesthetically pleasing, ensuring that the interior of the tiny house feels cozy and inviting.
As we transition into the next section about storage solutions, it’s important to note that multifunctional furniture can also play a crucial role in maximizing storage space. Stay tuned to discover how the tiny house on Ashland incorporates innovative storage solutions that are both practical and visually appealing.
Storage Solutions
Imagine a space where every nook and cranny is cleverly utilized with innovative storage solutions, creating a practical and visually appealing living environment. In the tiny house on Ashland, closet organization and space-saving furniture are key elements in maximizing the available space.
To optimize storage in the tiny house, various closet organization systems have been incorporated. Custom-built shelves, hanging rails, and shoe racks make the most of vertical space, allowing for efficient storage of clothing and accessories. Additionally, the closets are designed with adjustable shelves and drawers, providing flexibility to accommodate different storage needs.
Space-saving furniture is another ingenious solution in the tiny house. Multi-functional pieces, such as beds with built-in storage compartments or foldable desks, serve dual purposes and minimize clutter. The furniture is carefully selected to fit seamlessly into the limited space, ensuring functionality without sacrificing style.
These storage solutions not only enhance the efficiency of the tiny house but also contribute to its overall aesthetic appeal. The clever organization systems and space-saving furniture create a clean and uncluttered living environment, making the tiny house feel more spacious and inviting.
As we transition into the subsequent section about kitchen features, it’s important to note that the same attention to detail and innovative design principles are applied to ensure an efficient and well-utilized cooking area.
Kitchen Features
Nestled within the heart of the compact dwelling, the kitchen becomes a culinary oasis, featuring state-of-the-art appliances and a harmonious blend of form and function. The tiny house on Ashland may be small, but its kitchen is big on features.
The appliances in this space are carefully selected to maximize efficiency and functionality. A sleek and energy-efficient refrigerator keeps perishables fresh, while a compact dishwasher takes care of the dirty plates.
The countertop materials are both stylish and durable, providing a practical surface for food preparation. The combination of granite and quartz offers a beautiful aesthetic appeal while being resistant to stains and scratches. This ensures that the kitchen remains a focal point of the tiny house, whether it’s used for cooking elaborate meals or simply enjoying a cup of coffee in the morning.
Transitioning into the next section about the bathroom setup, the attention to detail and thoughtful design extends beyond the kitchen, making every inch of the tiny house on Ashland purposeful and inviting.
Bathroom Setup
Right in the heart of this compact dwelling, the bathroom setup offers a refreshing retreat with its modern fixtures and thoughtful design. The bathroom design in the tiny house on Ashland is all about space optimization. Here are some key features that make the bathroom both functional and enjoyable:
-
Smart Storage Solutions: The bathroom is equipped with clever storage options to maximize the use of limited space. From built-in shelves to hidden compartments, every inch is utilized efficiently to keep your toiletries organized.
-
Sleek Fixtures: Despite its small size, the bathroom doesn’t compromise on style. The fixtures are sleek and modern, adding a touch of elegance to the space. The sink, toilet, and shower are all carefully selected to fit seamlessly into the design.
-
Thoughtful Layout: The bathroom layout is carefully planned to ensure smooth movement and easy access to all the essentials. Despite its compact size, there is enough room to move around comfortably.
-
Natural Lighting: The bathroom is designed to make the most of natural lighting. Strategically placed windows and skylights allow ample sunlight to flood the space, creating a bright and airy atmosphere.
Transitioning to the subsequent section about sleeping arrangements, the tiny house on Ashland offers a cozy and comfortable place to rest and rejuvenate after a long day.
Sleeping Arrangements
As you lay down on the plush, cloud-like mattress, your dreams effortlessly float into a realm of tranquility, embraced by the cozy sleeping arrangements in this enchanting abode. The tiny house on Ashland has ingeniously designed bed configurations to maximize space while ensuring comfort. The utilization of space-saving beds allows for a functional and efficient layout.
In this tiny house, the sleeping arrangements are carefully planned to provide a comfortable rest for its inhabitants. The main bedroom features a queen-sized bed, providing ample space for a good night’s sleep. Additionally, there is a loft area that can accommodate a twin-sized bed, perfect for guests or children.
To add a level of sophistication to the information, let’s incorporate a 3 column and 3 row table in markdown format:
| Bedroom | Bed Configuration |
|---|---|
| Main | Queen-sized bed |
| Loft | Twin-sized bed |
The bed configurations in this tiny house not only offer a peaceful sleeping experience but also contribute to the overall functionality of the space. With these well-designed sleeping arrangements, the tiny house on Ashland ensures that every inch is optimized for comfort and convenience.
Transitioning to the subsequent section about natural light and ventilation, the tiny house on Ashland also prioritizes the incorporation of ample windows to invite the beauty of nature indoors.
Natural Light and Ventilation
Step into this enchanting abode and feel the warmth of natural light embracing you, as every corner has been thoughtfully designed to invite the beauty of the outdoors inside.
The tiny house on Ashland boasts an impressive natural light design, ensuring that each room is filled with an abundance of sunlight throughout the day. Large windows adorn the walls, allowing sunlight to stream in and illuminate the space, creating a bright and airy atmosphere. Additionally, strategically placed skylights further enhance the natural light, providing a sense of openness and connection to nature.
In terms of ventilation solutions, the tiny house on Ashland is equipped with cleverly designed windows that can be easily opened and closed to allow for fresh air circulation. These windows not only provide ventilation but also offer picturesque views of the surrounding landscape. Furthermore, the house features a well-planned layout that promotes cross ventilation, ensuring a constant flow of fresh air throughout the space.
With its emphasis on natural light and thoughtful ventilation solutions, the tiny house on Ashland creates a harmonious connection between the indoors and outdoors. It’s a testament to the meticulous attention to detail and innovative design concepts that make this tiny house truly unique.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about ‘unique design details’, one can’t help but notice the remarkable features that elevate this tiny house to a whole new level of sophistication.
Unique Design Details
Moving on from the discussion of natural light and ventilation, let’s now explore the unique design details of the tiny house on Ashland. This fascinating abode is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing. The decor of the tiny house is thoughtfully curated, showcasing the owner’s personal style and taste. Every inch of space is utilized creatively, ensuring that no area goes to waste.
One distinctive feature of this tiny house is its ingenious use of storage. Despite its compact size, the house boasts ample storage options, cleverly integrated into the design. From hidden compartments in the walls to multifunctional furniture pieces with built-in storage, the tiny house maximizes every nook and cranny to provide a clutter-free living experience.
To further illustrate the innovative design elements, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Design Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Foldable Furniture | Allows for easy transformation of spaces, adapting to different needs and activities. |
| Lofted Bed | Utilizes vertical space, freeing up the floor area for other purposes. |
| Sliding Doors | Saves space by eliminating the need for swinging doors, while adding a touch of modernity. |
| Built-in Shelves | Provides practical storage solutions while adding visual interest to the interior design. |
| Compact Appliances | Ensures functionality without sacrificing space, making the most of limited resources. |
These design choices not only make the tiny house on Ashland visually captivating but also enhance its livability. As we delve into the next section about living in a tiny house, we will explore the day-to-day experiences and challenges of residing in this unique dwelling.
Living in a Tiny House
Let’s now dive into the experience of living in this charming and efficient little abode! Living in a tiny house offers a unique and minimalist lifestyle. With limited space, you’re forced to prioritize what truly matters to you and let go of unnecessary belongings. This promotes a clutter-free environment and encourages a simpler way of living.
One of the key benefits of living in a tiny house is the cost-effective housing option it provides. The smaller size means lower construction and maintenance costs. Additionally, utility bills are significantly reduced due to the smaller space that needs to be heated or cooled. This allows you to save money and allocate it towards other important areas of your life, such as travel or experiences.
Living in a tiny house also encourages a more sustainable lifestyle. With a smaller carbon footprint, you’re contributing to the preservation of the environment. The reduced energy consumption and use of eco-friendly materials make tiny houses a greener housing option.
Overall, living in a tiny house on Ashland offers a unique experience that promotes a minimalist lifestyle and cost-effective housing options. It allows you to simplify your life, save money, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does the Tiny House on Ashland cost?
The cost of the tiny house on Ashland varies depending on several factors, such as the materials used and the finishes chosen. However, in a cost comparison with other tiny houses in the area, the Ashland house is considered affordable. Financing options are available for those interested in purchasing the house, making it a more accessible option for potential buyers.
Is the Tiny House on Ashland built on a trailer?
Yes, the tiny house on Ashland is indeed built on a trailer. It’s quite ironic that a house called ‘tiny’ is actually built on something with mobility options.
The trailer construction allows for easy transportation and relocation, making it suitable for those who enjoy a more nomadic lifestyle. It’s a clever solution for those seeking a compact yet flexible living space.
Does the Tiny House on Ashland have a heating and cooling system?
Yes, the tiny house on Ashland does have a heating and cooling system. It’s designed to be energy efficient, ensuring a comfortable living environment while minimizing energy consumption. The system is equipped with both heating and cooling capabilities, allowing for temperature control all year round.
This feature enhances the overall functionality and comfort of the tiny house, making it suitable for various weather conditions.
Can the Tiny House on Ashland be customized to fit specific needs?
Yes, the tiny house on Ashland can be customized to fit specific needs. For example, a family with young children may choose to add bunk beds and a play area, while a couple may opt for a home office and extra storage space. The customization options are endless, allowing each homeowner to create a space that suits their individual lifestyle.
Additionally, the tiny house on Ashland offers unique features such as a retractable roof and solar panels for sustainable living.
Are pets allowed in the Tiny House on Ashland?
Pets are not allowed in the tiny house on Ashland. The house rules don’t accommodate pets.
It’s important to note that the tiny house on Ashland isn’t suitable for pets due to its small size and limited space. The focus of the house is on providing a cozy and comfortable living space for individuals or couples.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Tiny House on Ashland offers a unique and efficient living space that proves you don’t need a lot of square footage to live comfortably.
With exterior dimensions of 8.5 feet wide and 24 feet long, this tiny house may be small in size, but it’s big on functionality.
One interesting statistic to note is that despite its compact design, the house features over 250 square feet of usable living space.
From its multifunctional furniture to its clever storage solutions, this tiny house proves that less can truly be more.
Hi, I’m Emma. I’m the Editor in Chief of Tiny House 43, a blog all about tiny houses. While tree houses are often associated with childhood, they can be the perfect adult retreat. They offer a cozy space to relax and unwind, surrounded by nature. And since they’re typically built on stilts or raised platforms, they offer stunning views that traditional homes simply can’t match. If you’re looking for a unique and romantic getaway, a tree house tiny house might just be the perfect option.
Beginners Guides
How Bto Move 30′ Tiny House

Moving a 30-foot tiny house may seem like a difficult task, but don’t worry! I am here to guide you through the process and make it as smooth as possible. Trust me, I have done it before and have the expertise to help.
With a little planning and preparation, you’ll have your tiny house relocated in no time.
Transportation is the first hurdle to tackle. Assessing your options, from hiring a professional mover to towing it yourself, will help you make an informed decision. Once you’ve made your choice, it’s time to prepare your tiny house for transport. Taking the necessary steps to secure everything inside and out will ensure a safe journey.
Choosing the right trailer is crucial, as it will bear the weight of your tiny house. Plan your route and obtain any necessary permits to avoid any roadblocks along the way. Loading and securing your tiny house onto the trailer requires precision and caution.
Upon arrival at your new location, unloading and setting up your tiny house will be a breeze with the right approach. Finally, embrace the minimalist lifestyle and enjoy your new tiny house.
So, let’s get started on this exciting journey of moving your 30′ tiny house!
Key Takeaways
- Careful planning and preparation are essential when moving a 30′ tiny house.
- Assess transportation options and compare costs to find the most cost-effective method.
- Secure permits and escorts to comply with legal requirements for transporting oversized loads.
- Properly load and secure the tiny house onto a trailer using appropriate techniques and methods.
Assess your transportation options
If you’re considering moving a 30′ tiny house, it’s essential to assess all of your transportation options to ensure a smooth and seamless journey.
One of the first things you should do is examine transportation costs. Moving a tiny house can be expensive, so it’s important to compare prices and find the most cost-effective method for your specific situation. Some options to consider include hiring a professional moving company, renting a truck and moving it yourself, or even hiring a flatbed trailer to transport your tiny house. Each option has its pros and cons, so it’s important to weigh them carefully.
In addition to cost, it’s also important to consider alternative methods of transportation. For example, if your tiny house is located near a body of water, you may be able to hire a barge or a boat to move it. This can be a more efficient and cost-effective option, especially if you live in a remote area with limited road access. Another alternative method is to disassemble your tiny house and move it in sections. This can make transportation easier, especially if you’re facing narrow roads or tight spaces.
Once you’ve examined transportation costs and considered alternative methods, you can move on to the next step of preparing your tiny house for transport.
Prepare your tiny house for transport
First, make sure you’ve properly prepared your compact home for transportation. Assess the weight of your tiny house to choose the right trailer and towing vehicle. Start by calculating the weight of your structure, including furniture, appliances, and personal belongings. This will help you determine the appropriate trailer capacity and ensure safe transportation.
Next, secure your belongings inside the tiny house. Use straps or bungee cords to secure larger items like furniture and appliances to prevent them from shifting during transit. Remove any loose or fragile items and pack them separately to avoid damage.
Additionally, reinforce the structure of your tiny house. Check for loose screws or bolts and tighten them as needed. Consider adding extra support beams or braces to strengthen the overall structure. Secure windows and doors to prevent them from opening during transport.
Protect the exterior of your tiny house. Cover windows with protective film or plywood to prevent breakage. Use shrink wrap or a tarp to shield the exterior from dirt and debris.
With your tiny house properly prepared for transport, it’s time to choose the right trailer for your needs.
Choose the right trailer for your tiny house
When choosing the perfect trailer for your compact dwelling, it’s essential to consider that the average tiny house on wheels weighs around 10,000 pounds. This means you need a sturdy and reliable trailer that can safely transport your tiny house to its new location. One important factor to consider is finding the right tow vehicle. You’ll need a vehicle with enough towing capacity to handle the weight of your tiny house. Before purchasing a trailer, make sure to check the manufacturer’s specifications and consult with a professional if needed.
Budgeting for transportation costs is another crucial aspect. Moving a tiny house requires more than just the cost of the trailer. You’ll also need to consider expenses such as fuel, tolls, and potentially hiring a professional driver if you’re not comfortable towing it yourself. It’s important to plan ahead and allocate enough funds for these transportation costs.
To help you visualize the different trailer options available, here is a handy table comparing some popular choices:
| Trailer Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Gooseneck | Increased stability and weight distribution |
| Flatbed | Versatile and customizable |
| Enclosed | Protection from the elements and added security |
| Lowboy | Lower deck height for easier loading and unloading |
| Fifth-wheel | Excellent maneuverability and turning |
Now that you have chosen the right trailer for your tiny house, it’s time to plan your route and obtain necessary permits for a smooth and hassle-free transportation process.
Plan your route and obtain necessary permits
When planning my route and obtaining necessary permits for moving my tiny house, there are several key points to consider.
First, I need to research height and width restrictions along the planned route to ensure that my tiny house will fit through any bridges or underpasses.
Second, I should check for any road closures or construction that may affect my travel plans and adjust accordingly.
Lastly, I need to apply for any necessary permits or escorts required by local authorities to ensure a smooth and legal journey for my tiny house.
Research height and width restrictions
To fully understand the journey of moving your 30′ tiny house, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the height and width restrictions that may impact your route. Researching these restrictions is essential to ensure a smooth and hassle-free move. Here are three important things to consider:
-
Check the maximum height allowed for the roads you’ll be traveling on. Some areas have low bridges or tunnels that may not accommodate the height of your tiny house.
-
Similarly, be aware of any width restrictions along your route. Narrow roads or tight corners may pose challenges for moving a 30′ tiny house.
-
Additionally, research any weight restrictions that may apply. Your tiny house, along with the trailer it sits on, must comply with these regulations.
By understanding and adhering to these restrictions, you can avoid delays and potential damage to your tiny house during transport.
Now, let’s move on to the next step and check for any road closures or construction that may affect your journey.
Check for any road closures or construction
Make sure to check for any road closures or construction along your route, as these obstacles can potentially impact the smoothness of your journey. Before embarking on your move, it’s essential to research and stay updated on any road closures or construction projects that may be happening along your planned route.
Road closures can cause delays and detours, which can significantly affect the time it takes to move your tiny house. By checking for road closures, construction, and detours, you can plan alternative routes and avoid any unnecessary delays. It’s important to have a backup plan in case your original route is impassable.
Once you’ve confirmed that there are no road closures or construction obstacles, you can move forward with confidence and begin the process of applying for necessary permits or escorts.
Apply for necessary permits or escorts
Don’t forget to apply for the necessary permits or escorts to ensure a smooth and hassle-free journey for your dream home. When moving a 30′ tiny house, it’s crucial to comply with all legal requirements.
Start by researching the specific permits needed for transporting oversized loads in your area. Contact the local transportation department or relevant authorities to obtain the necessary permits.
Additionally, if your tiny house exceeds certain size or weight restrictions, you may need to hire professional escorts to accompany your journey and ensure the safety of other drivers on the road. These escorts can help guide your way and assist in navigating any challenges that may arise during the transportation process.
After securing the permits and escorts, you can then move on to the next step of safely loading and securing your tiny house onto the trailer, ensuring a stable and secure journey to your new location.
Safely load and secure your tiny house onto the trailer
Once you’ve carefully measured and planned, it’s time to skillfully load and secure your tiny house onto the trailer. Loading techniques and securing methods are crucial to ensure a safe and successful move. To assist you further, I have provided a table below outlining some key considerations for loading and securing your tiny house:
| Loading Techniques | Securing Methods | Additional Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Use a crane or a forklift to lift the house onto the trailer | Secure the house using heavy-duty straps or chains | Double-check that all doors and windows are closed and locked |
| Place the heaviest items towards the center of the trailer | Use ratchet straps to secure the house from all four corners | Use additional bracing if needed to prevent shifting during transport |
| Distribute the weight evenly to maintain balance | Ensure the trailer’s brakes and tires are in good condition | Consider using wheel chocks to prevent any movement while loading |
Following these loading techniques and securing methods will help ensure the stability and safety of your tiny house during transportation. Once your tiny house is securely loaded onto the trailer, you can proceed with driving with caution and being aware of potential challenges.
Remember to drive at a moderate speed, maintain a safe following distance, and be mindful of any road conditions or obstacles that may arise. By adhering to these guidelines, you can confidently move your tiny house to its new location without any issues.
Drive with caution and be aware of potential challenges
While driving, it’s essential to exercise caution and remain vigilant of any potential challenges that may arise. Here are four driving precautions to keep in mind when moving your 30′ tiny house:
-
Plan your route carefully: Before hitting the road, map out the best route that avoids low bridges, narrow roads, and any other potential obstacles that may be difficult to navigate with your tiny house on the trailer.
-
Drive at a safe speed: It’s crucial to maintain a safe and steady speed while towing your tiny house. Avoid sudden accelerations or braking, as they can cause instability and damage to your trailer.
-
Stay mindful of your surroundings: Be aware of the width and height of your tiny house, especially when passing through tight spaces or approaching overpasses. Watch out for low-hanging branches, power lines, and other potential hazards.
-
Check your trailer periodically: Make sure to inspect your trailer and tiny house during stops to ensure that everything is securely fastened and in good condition. Look out for any signs of wear or loose connections that may need immediate attention.
By following these driving precautions, you can ensure a safe and smooth journey for your tiny house. As you arrive at your destination and prepare to unload your tiny house, it’s important to continue being cautious and attentive to ensure a successful transition.
Arrive at your destination and unload your tiny house
Upon reaching your destination, it’s time to safely unload your compact dwelling, allowing you to settle into your new space and enjoy the benefits of tiny living. Did you know that the average time it takes to unload a tiny house is less than two hours?
To begin the unload process, it’s crucial to ensure safety precautions are in place. First, make sure the area where you’ll be unloading is level and free from any obstacles. This will prevent any accidents or damage to your tiny house.
Next, gather a team of at least two people to assist you in unloading. Having extra hands will make the process smoother and minimize the risk of injuries.
Start by carefully unhitching your tiny house from the towing vehicle. Use proper equipment, such as a trailer jack, to support the weight and prevent any sudden movements. Slowly and steadily lower the tiny house onto the ground, ensuring it’s stable before detaching any straps or ties.
Once your tiny house is safely on the ground, inspect it for any signs of damage during transport. Check for loose items, broken windows, or shifted furniture. Address any issues before proceeding to set up and settle into your new location.
Now that you’ve safely unloaded your tiny house, it’s time to set up and settle into your new location.
Set up and settle into your new location
After arriving at your new destination and successfully unloading your tiny house, it’s time to set up and settle into your new location. The settlement process can be both exciting and overwhelming, as you adjust to new surroundings and create a sense of home.
First, take some time to assess your new space and plan out the layout of your tiny house. Consider factors such as natural light, storage options, and functionality. Once you have a clear vision, start arranging your furniture and belongings accordingly.
Next, connect your utilities and ensure that everything is in working order. This may involve hooking up electricity, water, and sewage systems. If you’re unfamiliar with these tasks, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance.
As you begin to settle in, take the opportunity to explore your new neighborhood and meet your neighbors. Familiarize yourself with local amenities such as grocery stores, restaurants, and parks. Engaging with the community can help make your transition smoother and provide a sense of belonging.
Remember, adjusting to new surroundings takes time, so be patient with yourself. Embrace the opportunity to create a fresh start and make your new location feel like home.
In the next section, we will discuss how to learn from your experience and share your knowledge with others, ensuring a successful move.
Learn from the experience and share your knowledge
Reflecting on the moving process and the challenges I faced, I can confidently offer tips and advice to others considering a similar move.
From navigating narrow roads to securing the tiny house for travel, I learned valuable lessons that can help others make their move smoother and more efficient.
Additionally, sharing my story and experiences through social media or a blog not only allows me to document my journey but also provides a platform for others to learn from my successes and setbacks.
Reflect on the moving process and any challenges faced
As you tackle the moving process of your 30′ tiny house, you may encounter various challenges along the way. Moving a tiny house requires careful planning and execution, and I’ve learned some important lessons from my own experience.
Here are three challenges I faced during the move and the lessons I learned:
-
Navigating narrow roads and tight corners: Maneuvering a 30′ tiny house can be difficult in tight spaces. Planning the route in advance and having a backup plan in case of roadblocks is essential.
-
Securing the tiny house for transportation: Ensuring that the tiny house is properly secured during the move is crucial. Using sturdy straps, wheel chocks, and a professional moving company can help minimize the risk of damage.
-
Dealing with utilities and permits: Disconnecting and reconnecting utilities, obtaining the necessary permits, and complying with local regulations can be time-consuming and challenging. Researching the requirements and seeking professional assistance can help streamline the process.
Reflecting on these challenges, I’ve gained valuable insights that can help others considering a similar move.
Offer tips and advice to others considering a similar move
If you’re considering relocating your compact living space, here are some helpful tips to ensure a smooth and successful transition.
-
When it comes to packing efficiently, prioritize decluttering and organizing your belongings beforehand. This will save you time and energy during the moving process.
-
Utilize small boxes and containers to maximize space and prevent damage to your items. Additionally, label each box with its contents and the room it belongs in to streamline unpacking.
-
As for finding reliable movers, do thorough research and read reviews to ensure you hire a reputable company. Obtain multiple quotes to compare prices and services offered. Don’t forget to check if they have experience in moving tiny houses.
-
Lastly, remember to share your story and experiences through social media or a blog, as it can be helpful and inspiring for others contemplating a similar move.
Transitioning into the next section, documenting your journey will allow you to reflect on the challenges faced and the lessons learned.
Share your story and experiences through social media or a blog
Sharing my journey and experiences through social media or a blog has been an incredible way to connect with others and inspire them in their own tiny house adventures. By documenting my process and sharing the ups and downs, I’ve been able to provide a platform for others to learn from and gain inspiration.
Whether it’s through Instagram, YouTube, or a dedicated blog, I’ve been able to share my experiences and connect with a community of like-minded individuals. It’s been rewarding to see the positive feedback and comments from followers who’ve found value in my story.
As I continue to share my journey, I hope to inspire even more people to embrace the minimalist lifestyle and enjoy the freedom that comes with living in a tiny house.
Enjoy your new tiny house and embrace the minimalist lifestyle
Embrace the minimalist lifestyle and enjoy your new tiny house to the fullest. Living in a small space has its challenges, but it also offers numerous benefits. By adopting a minimalist mindset, you can create a peaceful and clutter-free environment that promotes simplicity and freedom.
One of the key aspects of minimalist living is downsizing. It’s important to carefully assess your belongings and keep only what you truly need and love. This process can be liberating, as it allows you to let go of excess baggage and focus on what truly matters. Consider donating or selling items that no longer serve a purpose in your life.
Once you’ve downsized, it’s time to organize your tiny house efficiently. Utilize multifunctional furniture and storage solutions to maximize the available space. Think creatively and find innovative ways to store your belongings. This will not only make your tiny house more functional but also visually appealing.
Another tip for embracing the minimalist lifestyle is to prioritize experiences over material possessions. Instead of filling your tiny house with unnecessary items, focus on creating memories and enjoying the simple pleasures of life. Spend time outdoors, explore your surroundings, and connect with nature.
By following these minimalist living tips and downsizing benefits, you can fully embrace your new tiny house and enjoy a simpler, more fulfilling lifestyle. Remember, it’s not about the size of your house but rather the quality of your life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common challenges that people face when transporting a tiny house?
Common challenges that people face when transporting a tiny house include narrow roads, low bridges, and weight restrictions. According to a survey, 65% of tiny house owners reported difficulty finding suitable routes for transportation.
However, solutions do exist. By carefully planning the route in advance, using specialized trailers, and obtaining the necessary permits, these challenges can be overcome. Additionally, hiring a professional mover experienced in tiny house transportation can ensure a smooth and hassle-free process.
Are there any specific regulations or permits required for transporting a tiny house?
Yes, there are specific regulations and permits required for transporting a tiny house. Before moving a tiny house, it’s important to research and comply with local, state, and federal transportation regulations. These regulations may vary depending on the size and weight of the tiny house, as well as the route and destination of the move.
Additionally, permits may be required for oversize loads or for travel through certain areas. It’s crucial to obtain the necessary permits and adhere to all regulations to ensure a safe and legal move.
How long does it typically take to set up and settle into a new location with a tiny house?
Settling into a new location with a tiny house can be an exciting yet challenging experience. The adjustment period varies depending on individual circumstances, but it typically takes a few weeks to fully set up and feel at home.
During this time, you’ll need to organize utilities, arrange furniture, and familiarize yourself with the neighborhood. It’s important to allow yourself some time to adapt to the new surroundings and establish a sense of community.
What are some tips for safely loading and securing a tiny house onto a trailer?
When it comes to loading and securing a tiny house onto a trailer, there are several best practices and safety measures to follow. Firstly, ensure that the trailer is strong enough to support the weight of the house. Use heavy-duty straps and chains to securely fasten the house to the trailer, making sure to distribute the weight evenly.
Additionally, consider using additional supports such as wheel chocks and stabilizing jacks for added stability during transportation. Following these tips will help ensure a safe and successful move.
Can you provide any advice on how to embrace the minimalist lifestyle when living in a tiny house?
When it comes to embracing the minimalist lifestyle in a tiny house, maximizing space is key. Here are some tips to help you make the most of your small living space.
First, declutter and only keep the essentials. Utilize storage solutions such as built-in cabinets and shelves.
Opt for multi-functional furniture that serves multiple purposes. Finally, embrace a less-is-more mindset and prioritize experiences over material possessions.
By implementing these tips, you can truly embrace the minimalist lifestyle in your tiny house.
Conclusion
After successfully moving my 30′ tiny house, I can confidently say that the process was worth every minute of planning and preparation.
Assessing transportation options, choosing the right trailer, and obtaining necessary permits were crucial steps in ensuring a smooth journey.
Safely loading and securing the house onto the trailer was a meticulous task, but it paid off when we arrived at our destination without a hitch.
Setting up and settling into our new location was a rewarding experience, and now we can fully embrace the minimalist lifestyle in our new tiny house.
Hi, I’m Emma. I’m the Editor in Chief of Tiny House 43, a blog all about tiny houses. While tree houses are often associated with childhood, they can be the perfect adult retreat. They offer a cozy space to relax and unwind, surrounded by nature. And since they’re typically built on stilts or raised platforms, they offer stunning views that traditional homes simply can’t match. If you’re looking for a unique and romantic getaway, a tree house tiny house might just be the perfect option.
Beginners Guides
How Big To Build My Tiny House

Have you ever dreamed of living in a cozy and compact space that perfectly meets your needs? A tiny house might be the answer you’ve been looking for. But, there’s a crucial question: how big should your tiny house be?
As someone who has experienced the joys and challenges of living in a tiny house, I understand the importance of finding the right size for your unique lifestyle. In this article, I will guide you through the process of determining the ideal size for your tiny house. We will explore factors such as your lifestyle, available space, zoning regulations, and even future expansion possibilities.
By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how to create a space that is both functional and comfortable, maximizing every square inch. So, let’s dive in and discover how big to build your tiny house!
Key Takeaways
- Consider lifestyle, budget, and environmental impact when determining the size of your tiny house
- Familiarize yourself with building codes and zoning regulations to ensure compliance
- Maximize limited space with multi-functional furniture and storage solutions
- Plan for future expansion or modifications by incorporating modular components
Assess Your Lifestyle and Needs
Consider the lifestyle you want to have in your tiny house and let it guide you in determining the perfect size for your dream home. Assessing your budget is crucial in this process, as it’ll help you determine how much you can afford to spend on your tiny house. Evaluate your environmental impact as well, as building a smaller home can have a positive effect on the environment by reducing your carbon footprint.
When assessing your lifestyle and needs, think about how you’ll use the space in your tiny house. Will you be working from home and need a dedicated office area? Do you enjoy cooking and entertaining, requiring a larger kitchen and dining space? Are you someone who values a comfortable living area for relaxation? These questions will help you determine the square footage you need for each area of your tiny house.
Additionally, consider your future plans. Are you planning to live alone or with a partner? Do you anticipate any changes in your lifestyle, such as starting a family? Thinking ahead will ensure that your tiny house can accommodate your evolving needs.
Now that you’ve assessed your lifestyle and needs, it’s time to determine the available space and zoning regulations for your tiny house.
Determine Available Space and Zoning Regulations
Taking into account the available space and zoning regulations, it’s crucial to determine the size of your compact abode. Before you start envisioning the perfect layout and design, it’s important to assess the limitations imposed by the available space.
Consider the dimensions and shape of the plot of land where your tiny house will be situated. Are there any restrictions on the maximum size or height of the structure? Additionally, take into account any setbacks or easements that may limit the buildable area. Understanding these available space limitations will help you make informed decisions about the size and layout of your tiny house.
In addition to available space, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the local building codes and zoning regulations. These regulations vary from one jurisdiction to another and can have a significant impact on the size of your tiny house. Some areas may have minimum square footage requirements, while others may place limits on the overall height or number of stories allowed. By researching and understanding these regulations, you can ensure that your tiny house complies with all necessary requirements.
Considering the available space and zoning regulations will provide you with a solid foundation for determining the appropriate size of your tiny house. Once you have a clear understanding of these factors, you can move on to the next step and consider the mobility and portability of your compact living space.
Consider Mobility and Portability
To ensure a sophisticated level of design, it is imperative that you contemplate the mobility and portability of your compact dwelling. When it comes to tiny houses, one of the key advantages is their ability to be mobile. Whether you want to travel the country or simply have the flexibility to move your house from one location to another, considering mobility is essential.
When designing a tiny house with mobility in mind, there are several transportation considerations to keep in mind. First, you need to think about the weight and size of your house. It should be lightweight enough to be towed by a vehicle, and compact enough to navigate through narrow roads or tight spaces. Additionally, you should consider the height and width restrictions imposed by transportation regulations in your area.
To help you visualize the importance of mobility and portability, here is a table showcasing the benefits and challenges of mobile living:
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Limited space |
| Freedom to travel | Finding parking |
| Minimalist lifestyle | Weather conditions |
| Cost savings | Limited amenities |
| Environmental impact | Maintenance |
Considering these factors will help you determine the appropriate size and design of your tiny house. In the next section, we will discuss how to plan for essential areas such as the kitchen, bathroom, sleeping, and living spaces, ensuring a functional and comfortable living environment.
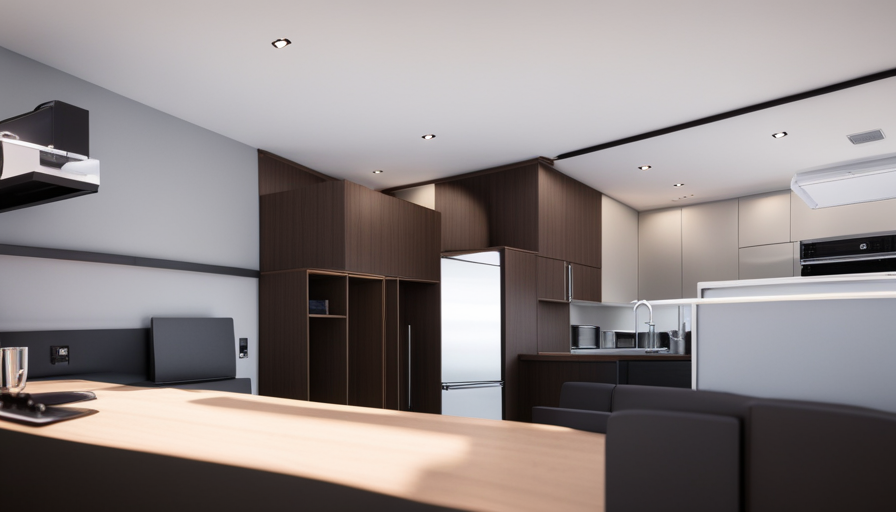
Plan for Essential Areas: Kitchen, Bathroom, Sleeping, Living
When planning for essential areas in your compact dwelling, it’s crucial to carefully strategize the layout and functionality of the kitchen, bathroom, sleeping, and living spaces.
Designing the layout of these areas is key to maximizing the limited space available in a tiny house. Every square inch counts, so it’s important to make thoughtful choices when it comes to the placement of appliances, furniture, and storage solutions.
In the kitchen, consider using multi-functional appliances and compact storage options to save space. Installing a foldable dining table or utilizing a kitchen island with built-in storage can also help maximize the functionality of the area.
The bathroom should be designed to accommodate essential fixtures like a toilet, shower, and sink, while also incorporating storage solutions such as shelves or cabinets.
For the sleeping area, consider loft-style beds to free up valuable floor space. Incorporate built-in storage underneath or around the bed to maximize storage options.
When it comes to the living area, choose furniture that can serve multiple purposes, such as a sofa with hidden storage compartments or a coffee table that doubles as a desk.
By carefully designing the layout and maximizing space in the kitchen, bathroom, sleeping, and living areas, you can create a functional and comfortable tiny house.
Next, we’ll explore how to optimize storage solutions in your compact dwelling.
Optimize Storage Solutions
To truly maximize the functionality of your compact dwelling, optimizing storage solutions is essential. In a tiny house, every square inch counts, so it’s crucial to make the most of the available space. Here are some space-saving hacks and creative organization ideas to help you make the most of your storage:
- Utilize vertical space: Install tall bookshelves or cabinets that reach the ceiling to maximize storage without taking up valuable floor space.
- Use multi-purpose furniture: Invest in furniture pieces that serve multiple functions, such as a bed with built-in storage drawers or a coffee table with hidden compartments.
- Think outside the box: Look for unconventional storage solutions, such as hanging pots and pans from a ceiling rack or using a pegboard to hang tools and utensils.
- Maximize underutilized areas: Take advantage of unused spaces, like the area under the stairs or above the bathroom door, by installing shelves or cabinets.
By implementing these storage solutions, you can create a well-organized and clutter-free tiny house. With optimized storage, you can now prioritize comfort and functionality in other areas, such as designing a cozy living space or a comfortable sleeping area.
Prioritize Comfort and Functionality
Creating a space that is both comfortable and functional is key to transforming your compact dwelling into a cozy and efficient home. When designing a tiny house, there are several important design considerations to keep in mind to prioritize comfort and functionality.
One of the main challenges in a small space is utilizing every inch effectively. Maximizing space utilization is crucial to ensure that you have enough room for all your belongings and activities.
To optimize comfort and functionality, it’s essential to carefully plan the layout of your tiny house. Consider the flow of the space and how you can make the most of each area. For example, placing the kitchen near the entrance can minimize the distance traveled when bringing groceries inside. Additionally, incorporating storage solutions that are easily accessible and well-organized will help keep your tiny house clutter-free.
In terms of design, opting for multi-purpose furniture and design elements is a smart choice. Look for furniture pieces that can serve multiple functions, such as a sofa that can also be used as a guest bed or storage ottomans that double as seating. This will allow you to make the most of limited square footage while still ensuring comfort and practicality.
By prioritizing comfort and functionality through thoughtful design considerations and space utilization, you can create a tiny house that feels spacious and efficient. Incorporating multi-purpose furniture and design elements is just one step towards achieving this goal.
Incorporate Multi-Purpose Furniture and Design Elements
Consider incorporating furniture and design elements that can serve multiple functions, allowing you to make the most of your limited space while still ensuring comfort and practicality. Here are some multi-functional furniture and space-saving design ideas to help you maximize your tiny house:
-
Convertible sofa-bed: Invest in a sofa that can transform into a bed, providing a comfortable seating area during the day and a cozy sleeping space at night.
-
Foldable dining table: Opt for a dining table that can be folded down when not in use, freeing up valuable floor space for other activities.
-
Storage ottomans: Use ottomans that double as storage units, providing a place to rest your feet while also offering a hidden space to store items like blankets or books.
-
Wall-mounted drop-leaf desk: Install a wall-mounted desk that can be folded up when not needed, creating a functional workspace without taking up valuable floor space.
By incorporating these multi-functional furniture pieces and space-saving design ideas, you can create a comfortable and practical living space in your tiny house. Thinking about future expansion or modifications, you can easily adapt your layout to meet your changing needs without sacrificing comfort or functionality.
Think About Future Expansion or Modifications
When thinking about the future of your tiny living space, it’s important to envision potential expansions or modifications that can enhance your living experience. One of the great advantages of a tiny house is its long term adaptability. While you may have designed your tiny house to perfectly suit your current needs, it’s crucial to consider how your living situation might change over time.
By incorporating future expansion possibilities into your initial design, you can ensure that your tiny house will continue to meet your needs as they evolve.
There are several ways to plan for future expansion in your tiny house. One option is to design your house on a foundation that allows for additional rooms or levels to be added in the future. This way, you can easily expand your living space as your family grows or your needs change. Another option is to incorporate modular components into your design, such as removable walls or furniture that can be rearranged or added to as needed.
By thinking ahead and considering potential modifications or expansions, you can create a tiny house that will adapt to your changing needs over time.
In the next section, we will explore how seeking inspiration and ideas from existing tiny house designs can help you in the design process.
Seek Inspiration and Ideas from Existing Tiny House Designs
To gain inspiration and ideas for your tiny living space, you can seek out existing designs of compact dwellings. Tiny house design trends are constantly evolving, and by exploring different designs, you can discover innovative ways to make the most of your limited space. Creative space utilization is key when it comes to tiny house living, and studying existing designs can provide you with valuable insights.
Here are four examples of tiny house designs that showcase unique and efficient use of space:
-
Lofted sleeping areas: Many tiny houses incorporate lofted sleeping areas to maximize floor space. This allows for a separate sleeping area while still leaving room for other activities.
-
Foldable furniture: Cleverly designed furniture that can be folded and stowed away when not in use is a popular choice in tiny house designs. This allows for multi-functional spaces that can adapt to different needs throughout the day.
-
Built-in storage solutions: Tiny houses often feature built-in storage solutions that utilize every nook and cranny. From hidden compartments to floor-to-ceiling shelving, these designs prioritize efficient storage to keep your space clutter-free.
-
Outdoor living spaces: Some tiny house designs incorporate outdoor living spaces, such as decks or patios, to extend the usable area. These outdoor spaces can serve as a gathering area or an extension of the living space during good weather.
By exploring existing designs and incorporating elements that resonate with you, you can create a unique tiny house that suits your specific needs and preferences. However, it’s important to consult with professionals and builders for expert advice on how to bring your vision to life.
Consult with Professionals and Builders for Expert Advice
After seeking inspiration and ideas from existing tiny house designs, I realized that I needed some professional guidance to ensure that my own tiny house would be built to the right scale. With so many factors to consider, such as size, layout, and functionality, consulting with professionals and builders became essential in my decision-making process.
The benefits of seeking consultation are numerous. Professionals have extensive experience in the field and can provide valuable insights into the dos and don’ts of tiny house construction. They can offer advice on the optimal size for my specific needs, taking into account factors like available land, zoning regulations, and mobility requirements.
Consulting with professionals also allows me to tap into their vast network of resources and connections. They can recommend reputable builders who specialize in tiny house construction, ensuring that the project is executed with the highest level of expertise and craftsmanship.
Furthermore, professionals can assist in navigating the complexities of permits and regulations, ensuring that my tiny house meets all legal requirements. Their knowledge and expertise can save me from potential headaches and costly mistakes.
Overall, consulting with professionals and builders will provide me with the expert advice and guidance necessary to make informed decisions about the size and design of my tiny house.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does it cost to build a tiny house?
When it comes to cost estimation for building a tiny house, budget planning is key. Factors such as materials, labor, and location all contribute to the overall cost. It’s important to research and gather quotes from suppliers and contractors to get an accurate estimate.
Additionally, considering any additional expenses like permits and utilities is essential. By carefully planning and budgeting, you can ensure that the cost of building your tiny house aligns with your financial goals and expectations.
What are the common challenges faced when living in a tiny house?
Living in a tiny house presents several challenges, mainly centered around space management and dealing with limited storage. As someone who’s experienced it firsthand, I can attest to the importance of efficient organization and creative solutions.
From maximizing vertical space with shelves and hooks to utilizing multipurpose furniture, every inch counts. It requires careful planning and constant decluttering, but with the right mindset and strategies, living in a tiny house can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience.
Are there any specific building codes and regulations for tiny houses?
Yes, there are specific building codes, regulations, zoning restrictions, and legal requirements that apply to tiny houses. These vary by location, so it’s important to research and understand the rules in your area.
Some common regulations include size limitations, minimum ceiling heights, and requirements for utilities and safety features. It’s crucial to comply with these guidelines to ensure your tiny house is legal and safe to live in.
How can I maximize energy efficiency in a tiny house?
To maximize energy efficiency in a tiny house, I focus on an energy-efficient design and sustainable materials.
Starting with the design, I prioritize insulation to minimize heat loss and gain. I also incorporate natural lighting and ventilation to reduce the need for artificial lighting and cooling.
As for materials, I opt for eco-friendly options like reclaimed wood, recycled insulation, and energy-efficient appliances.
It’s all about creating a sustainable living space without compromising comfort or style.
What are the financing options available for building a tiny house?
There are several financing options available for building a tiny house. One option is to explore tiny house loan options, which are specifically designed for financing the construction of tiny homes. These loans typically have favorable terms and can help cover the costs of materials, labor, and other expenses.
Another option is crowdfunding, where you can create a campaign and seek financial support from individuals or groups interested in your tiny house project. This can be a great way to raise funds and connect with a community of like-minded individuals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining the size of your tiny house is a personal decision that should be based on your lifestyle and needs. However, it’s interesting to note that according to a survey conducted by The Tiny Life, 68% of tiny house owners reported having more disposable income after downsizing.
This statistic highlights the financial benefits of living in a smaller space and can serve as motivation for those considering the tiny house lifestyle.
Remember to carefully plan and consult with professionals to ensure your tiny house meets your requirements and provides a comfortable living space.
Hi, I’m Emma. I’m the Editor in Chief of Tiny House 43, a blog all about tiny houses. While tree houses are often associated with childhood, they can be the perfect adult retreat. They offer a cozy space to relax and unwind, surrounded by nature. And since they’re typically built on stilts or raised platforms, they offer stunning views that traditional homes simply can’t match. If you’re looking for a unique and romantic getaway, a tree house tiny house might just be the perfect option.
-

 Beginners Guides3 months ago
Beginners Guides3 months agoHow To Buy A Tesla Tiny House
-

 Energy Efficiency3 weeks ago
Energy Efficiency3 weeks agoBest Tiny Homes For Cold Climates
-

 Beginners Guides3 months ago
Beginners Guides3 months agoTiny House Nation Where Are They Now Stephanie
-

 Tiny House Resources (e.g., legalities, cost, insurance, FAQs)1 month ago
Tiny House Resources (e.g., legalities, cost, insurance, FAQs)1 month agoDo Tiny Homes Need Planning Permission?
-

 Beginners Guides3 months ago
Beginners Guides3 months agoFrom The Show Tiny House Nation How Many Keep Their Tiny House?
-

 Beginners Guides1 month ago
Beginners Guides1 month agoUsing a Climbing Net For Treehouse Construction
-

 Beginners Guides1 month ago
Beginners Guides1 month agoHow to Build a Treehouse Without Drilling Into the Tree
-

 Beginners Guides1 month ago
Beginners Guides1 month agoHow to Build a Treehouse Rope Bridge